Independent Component Analysis for Emerging Technique in Brain Signal Processing
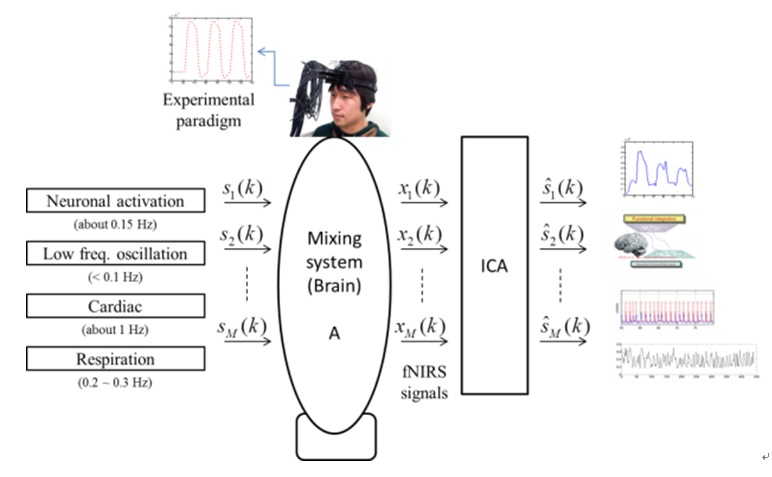
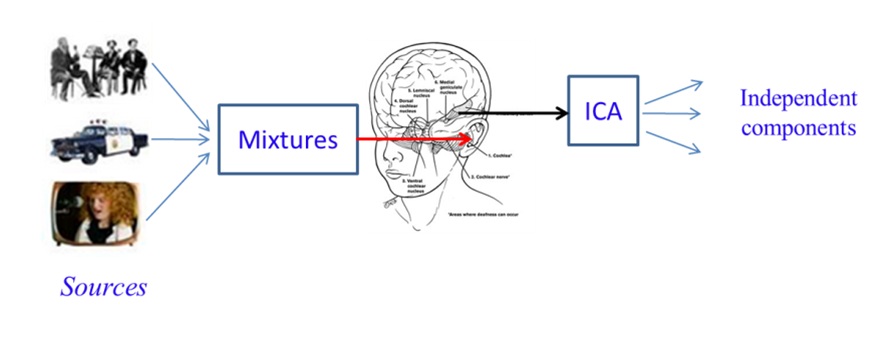
In this research, we investigate the independent component analysis (ICA) in analyzing the source brain signals. The ICA has been utilized by many researchers in brain engineering fields including electroencephalography (EEG), functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS), functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI). The ICA has been a good technique to obtain the independent components of the unobservable source signals. Using the ICA method, it can enhance the detection of brain signals, in which the signal to noise ratio are increased during the particular tasks than while resting.
[Independent component analysis]
Hemodynamic response in the human auditory cortex
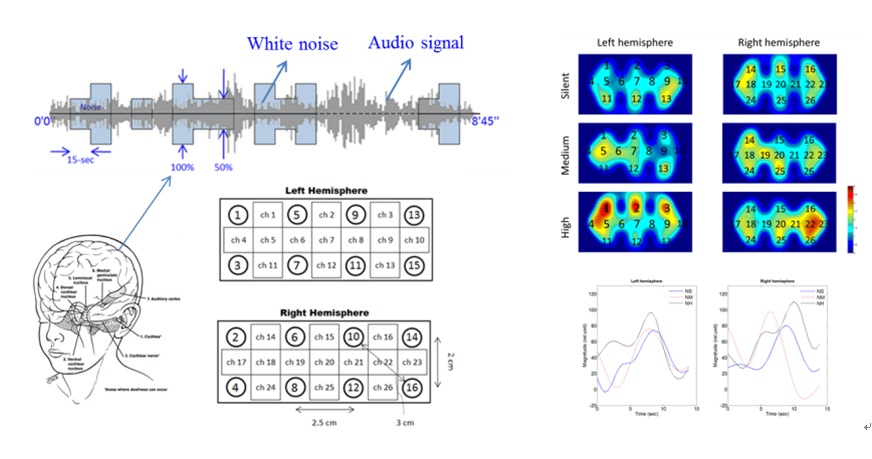
In humans, the brain asymmetry has been observed in terms of anatomy and function. The lateralization auditory cortex of the left hemisphere for speech processing and right hemisphere for music processing was one the earliest observation of brain asymmetry. In this research, we investigate the effects of different tasks in auditory cortex activation using functional near-infrared spectroscopy.
[Experimental paradigm and results of audio cortex activation]
Human can be able to focus one’s listening attention on a single stimulus among many conversations and background noise. In the second part, we investigate the hemodynamic response to reconstruct various audio stimuli.
Lorem ipsum dolor sit amet, facilis ocurreret vim ei, id sea magna populo sanctus. Ut usu altera phaedrum, ceteros albucius at eos. Ad prima ubique oblique ius. Vel no dolorem iudicabit consetetur. Vis tibique convenire ad, sit et erat congue euismod. Pri an noster placerat, in appareat abhorreant eloquentiam usu, qui ei sale scripta fuisset. Ridens officiis deterruisset eam id, usu et sanctus definitiones, alia elaboraret per ei. Pri epicurei recteque theophrastus eu, est clita platonem et. Est et essent eirmod, et has decore adolescens, eam et nibh sanctus. Alterum denique propriae ut cum, ut suas dicunt percipit sea, per ut sint augue.
[Reconstructing audio stimuli from human auditory corte x]