DEVELOPMENT OF fNIRS SYSTEM
In the wake of recent advances in the field of neuroscience, functional near-infrared spectroscopy (fNIRS) has been widely used to measure the concentration changes in the blood chromophores during mental activity. fNIRS system can be constructed low cost, portable and easy to use. Given that approximately 80% of blood chromophores are water, it is particularly important to identify the effect of water concentration change on measurement data.
[fNIRS system diagram]
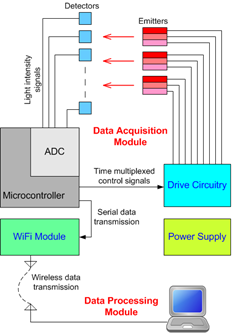
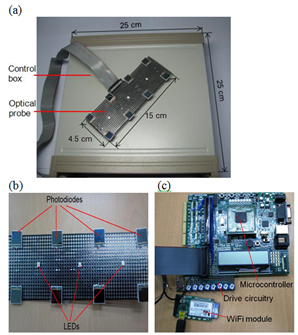
In Cognocontrol lab, we have developed a wireless fNIRS system that detects not only the concentration changes of oxy-hemoglobin (HbO) and deoxy-hemoglobin (HbR) during mental activity but also that of water (H2O); additionally, it implements a water-correction algorithm that improves the HbO and HbR signal strengths manifest during an arithmetic task. The system comprises a microcontroller, an optical probe, tri-wavelength light emitting diodes, photodiodes, a WiFi communication module and a battery.
[Wireless LED-based fNIRS system]
For more details, see “Note: Three wavelengths near-infrared spectroscopy system for compensating the light absorbance by water,” Review of Scientific Instruments , Vol. 85, No. 2 , AN: 026111, pp. 1-3 , February 2014.
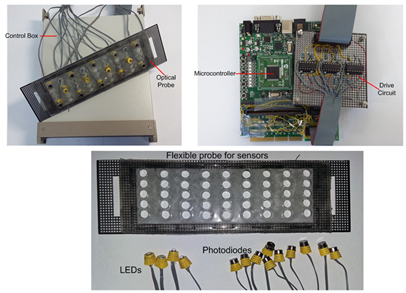
Currently we are working on the hybrid fNIRS-EEG system to acquire optical and electrical brain signals simultaneously. A flexible probe is designed and implemented in such a way that it can accommodate both the EEG sensors and the fNIRS optodes. The control unit controls the switching between different wavelengths of LEDs and the activation of the respective photodiodes. MATLAB based software has been developed to acquire data from the system and then plot temporal and spatial data in real time. For offline processing of data, separate software has been developed in MATLAB.
[Hybrid EEG-fNIRS system]